1. Introduction
Definition and Overview
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant naturally produced in the cells of the human body. It is composed of three amino acids: glutamine, cysteine, and glycine. As an essential molecule, it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including detoxification, immune system support, and cellular repair.
Importance of Glutathione
Often referred to as the "master antioxidant," glutathione is vital for maintaining overall health. Its ability to neutralize free radicals and reactive oxygen species makes it indispensable in protecting the body from oxidative stress and related diseases.
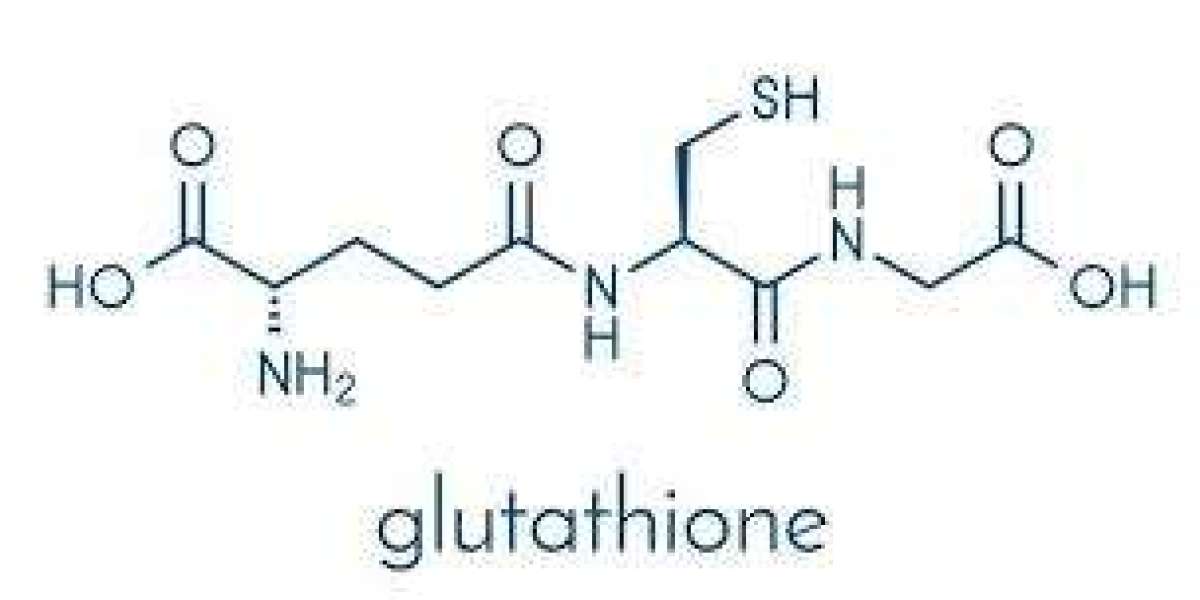
2. What is Glutathione?
Chemical Structure
Glutathione is a tripeptide, consisting of three amino acids—glutamine, cysteine, and glycine. This unique structure allows it to perform several essential functions within the body, particularly in detoxification processes and immune system enhancement.
How it Functions in the Body
Glutathione works by donating electrons to unstable molecules, known as free radicals, neutralizing them and preventing cellular damage. It also plays a key role in recycling other antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, further enhancing the body's defense mechanisms.
3. Sources of Glutathione
Natural Sources
Glutathione is found in various foods, particularly those rich in sulfur, such as garlic, onions, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower. Additionally, fruits like avocados, and meats like chicken and fish, are also good sources.
Dietary Supplements
To boost glutathione levels, many people turn to supplements, which come in various forms, including oral capsules, sublingual tablets, and intravenous injections. These supplements can be especially beneficial for individuals with low glutathione levels due to aging or chronic illness.
4. Health Benefits of Glutathione
Antioxidant Properties
As a potent antioxidant, glutathione protects cells from damage caused by oxidative stress. This function is crucial in preventing chronic diseases, including cancer and heart disease, by reducing the oxidative damage that can lead to cell mutation and inflammation.
Detoxification Support
Glutathione plays a critical role in detoxifying the body by binding to toxins and facilitating their excretion. This process is particularly important for liver health, as the liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxification.
Immune System Enhancement
By supporting the immune system, glutathione helps the body fight off infections and other illnesses. It enhances the activity of immune cells, including lymphocytes and natural killer cells, thereby boosting the body's ability to combat pathogens.
5. Role in Cellular Health
Protection Against Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Glutathione helps restore this balance, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
DNA Repair and Cell Regeneration
Glutathione is also involved in DNA repair and cell regeneration, processes that are vital for maintaining cellular health and preventing mutations that can lead to cancer and other diseases.
6. Glutathione and Aging
Anti-Aging Effects
As we age, our glutathione levels naturally decline, leading to increased oxidative stress and a higher risk of chronic diseases. Supplementing with glutathione can help slow the aging process by reducing oxidative damage and supporting cellular health.
Skin Health
Glutathione is often used in skin care for its ability to lighten the skin by reducing melanin production. It also helps in reducing wrinkles and improving skin elasticity by neutralizing free radicals that cause skin aging.
7. Glutathione in Chronic Diseases
Role in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
Glutathione plays a dual role in cancer prevention and treatment. While it protects healthy cells from oxidative damage, it can also protect cancer cells from chemotherapy. This dual role necessitates careful management in clinical settings.
Impact on Heart Health
By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, glutathione helps protect the heart from damage, potentially lowering the risk of heart disease. Its role in detoxification also supports overall cardiovascular health.
Effects on Liver Health
The liver relies heavily on glutathione for detoxification. Adequate levels of glutathione are essential for liver function, and deficiencies are linked to liver diseases, including fatty liver disease and cirrhosis.
8. Glutathione Deficiency
Causes and Risk Factors
Glutathione deficiency can result from various factors, including poor diet, chronic stress, and exposure to toxins. Aging is another significant risk factor, as the body's ability to produce glutathione declines with age.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of glutathione deficiency include fatigue, frequent infections, and unexplained aches and pains. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure glutathione levels and assess overall antioxidant status.
9. Increasing Glutathione Levels
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
Consuming a diet rich in glutathione-boosting foods, such as sulfur-rich vegetables, can help increase levels naturally. Regular exercise and stress management techniques also support glutathione production.
Role of Supplements and Injections
For those with low levels of glutathione, supplements and injections can be effective in raising levels quickly. However, it's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation, as high doses can have side effects.
10. Safety and Side Effects
Potential Side Effects
While glutathione is generally safe for most people, some may experience side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions. It's crucial to follow dosing recommendations to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Contraindications
Individuals with certain health conditions, such as asthma or liver disease, should exercise caution when using glutathione supplements, as it may exacerbate these conditions. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
11. Expert Insights
Quotes from Health Professionals
Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in antioxidant therapy, states, "Glutathione is crucial for maintaining cellular health and preventing oxidative stress. Its role in detoxification cannot be overstated, particularly in our modern world filled with environmental toxins."
Case Studies on Glutathione Use
In a recent case study, patients with chronic liver disease who received glutathione supplementation showed significant improvements in liver function tests, highlighting its potential as a supportive therapy in liver health management.
12. Future Outlook
Emerging Research and Trends
Ongoing research into glutathione is uncovering new potential applications, from enhancing athletic performance to improving mental health. As our understanding of this molecule grows, so too does its potential in various fields of medicine.
Potential Future Applications
Future applications of glutathione may include its use in personalized medicine, where it could be tailored to individual needs based on genetic profiles and specific health conditions.
13. Practical Applications
Incorporating Glutathione into Daily Life
Incorporating glutathione into daily life can be as simple as eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, which depletes glutathione levels.
Tips for Optimizing Glutathione Levels
To optimize glutathione levels, consider adding foods like garlic, spinach, and avocados to your diet, along with regular physical activity. For those with specific health concerns, supplements may be necessary, but only under professional guidance.
14. FAQs
Common Questions and Answers
What does glutathione do in the body? Glutathione acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from damage and supporting detoxification.
Can you take glutathione supplements daily? Yes, but it's important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure it's appropriate for your needs.
Does glutathione lighten the skin? Yes, it can reduce melanin production, leading to a lighter skin tone over time.
15. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Glutathione is a critical antioxidant that plays numerous roles in maintaining health, from detoxification to immune support. Understanding its functions and benefits can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
Final Thoughts
Incorporating glutathione into your health regimen, whether through diet, lifestyle changes, or supplementation, can provide significant benefits. As research continues to evolve, its importance in health and wellness becomes increasingly clear.